Home — What Is a SERP? A Guide to Search Engine Results Pages
What Is a SERP? A Guide to Search Engine Results Pages
There are millions of pages on the web, but none are more important to digital marketers than search engine results pages, or SERPs. In this beginner’s guide to SERPs, you’ll learn all about why they’re so important for SEO, and how exactly a SERP works.
Search engine optimization specialists and PPC advertisers both want the same valuable real estate in the most prominent parts of the SERPs, but competition is fierce. Changes in search mean it’s more important than ever for digital marketers to know how search works and what they can do to maximize their visibility.
Example of a Google SERP (Page 1 is where you want to be!)
What is a SERP?
SERP stands for search engine results page. Search engine results pages are web pages served to users when they search for something online using a search engine, such as Google. The user enters their search query (often using specific terms and phrases known as keywords), then the search engine presents them with a SERP. These are the most relevant, high-quality results, including organic pages and sponsored ads, related to the search query.
Every SERP is unique, even for search queries performed on the same search engine using the same keywords or search queries. This is because virtually all search engines customize the experience for their users by presenting results based on a wide range of factors beyond their search terms, such as the user’s physical location, browsing history, and social settings. Search rankings are also constantly in flux, as new content appears on the web and as search engines change their algorithms. Two SERPs may appear identical, and contain many of the same results, but will often feature subtle differences.
How do SERPs work?
The appearance of search engine results pages is constantly in flux due to experiments conducted by Google, Bing, and other search engine providers to offer their users a more intuitive, responsive experience. This, combined with emerging and rapidly developing technologies in the search space, mean that the SERPs of today differ greatly in appearance from their older predecessors.
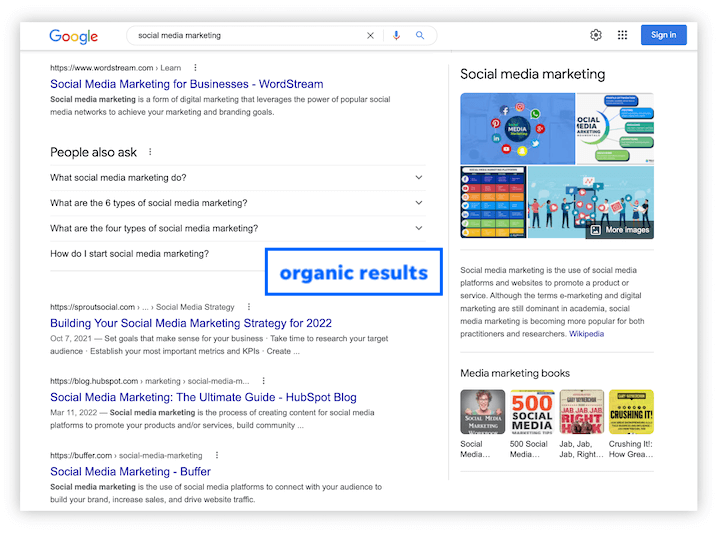
Organic Results on the SERP
SERPs typically contain two types of content – “organic” results and paid results. Organic results are listings of web pages that appear as a result of the search engine’s algorithm (more on this shortly). Search engine optimization professionals, commonly known as SEOs, specialize in optimizing web content and websites to rank more highly in organic search results.
In the following figure, the highlighted results are all organic results:

Organic results on the SERP
The box on the right side of this SERP is known as the Knowledge Graph (also sometimes called the Knowledge Box). This is a feature that Google introduced in 2012 that pulls data to commonly asked questions from sources across the web to provide concise answers to questions in one central location on the SERP. In this case, you can see a wide range of information about Abraham Lincoln, such as the date and place of his birth, his height, the date on which he was assassinated, his political affiliation, and the names of his children – many of which facts have their own links to the relevant pages.
Some SERPs will feature significantly more organic results than others, such as the example above. This is due to the differing intent of various searches. There are three primary types of Internet search:
- Informational
- Navigational
- Transactional
Informational searches are those in which the user hopes to find information on a given topic, such as Abraham Lincoln. It wouldn’t make much sense to place ads or other types of paid results on a SERP like this, as the search query “Abraham Lincoln” has very low commercial intent; the vast majority of searchers using this search query are not looking to buy something, and as such only informational results are displayed on the SERP.
Navigational queries are those in which the user hopes to locate a specific website through their search. This may be the case for individuals searching for a specific website, trying to locate a website whose URL they can no longer remember, or another type of navigational objective.
Finally, transactional searches are those in which paid results are most likely to be displayed on the SERP. Transactional searches have high commercial intent, and search queries leading to transactional SERPs may include keywords such as “buy” and other terms that suggest a strong desire to make a purchase.
Find the best keywords to target for your business with our Free Keyword Tool.
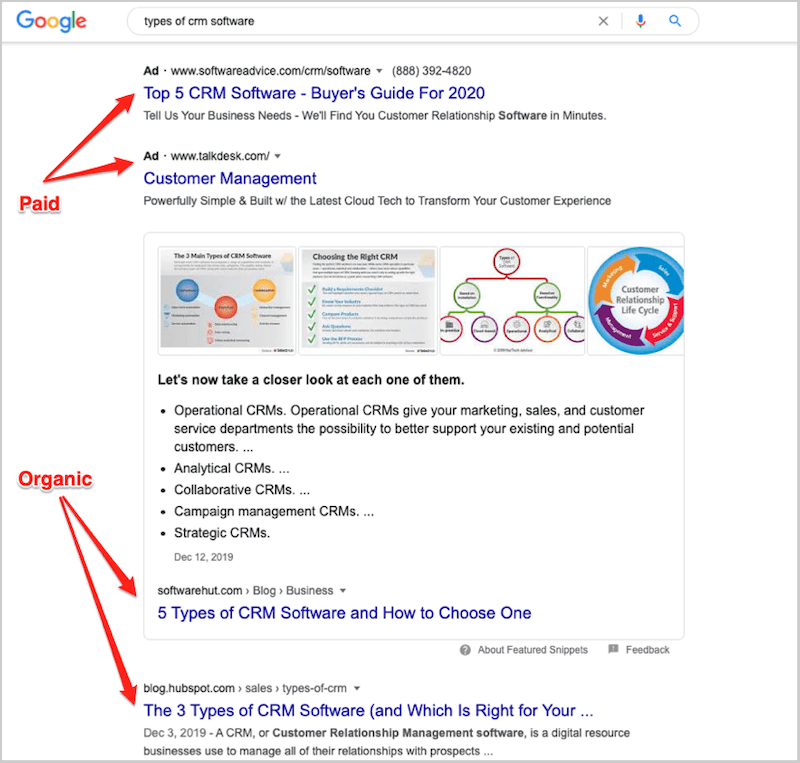
Paid Results on the SERP
In contrast to organic results, paid results are those that have been paid to be displayed by an advertiser. In the past, paid results were almost exclusively limited to small, text-based ads that were typically displayed above and to the right of the organic results. Today, however, paid results can take a wide range of forms, and there are dozens of advertising formats that cater to the needs of advertisers.
Some paid results on the Google SERP
In the example above (a SERP for the search query “lawnmowers”), all of the results on the SERP – with the exception of the map and business listing beneath it – are paid results. The three large text-based ads at the top of the SERP (considered prime positioning for advertisers) are typical PPC ads. Of those three ads, the lower two (for Craftsman.com and Husqvarna.com) both feature ad extensions allowing prospective customers to navigate to specific pages on their websites directly from the ads.
The image-based ads on the right of the page are Shopping ads, a feature offered on the Google Ads platform that allows ecommerce retailers’ product information to be displayed alongside other results on the SERP. Shopping ads can contain a wide range of information, such as product availability, user reviews, special offers, and more.
There are two additional PPC ads directly beneath the Shopping ads (as indicated by the yellow “Ads” flag above them) that also feature the user review ad extensions, indicated by the star ratings directly beneath the destination URL.
The map and business listing are the only results on this SERP that are not explicitly paid results. This map is shown based on a user’s location, and feature listings for local businesses that have set up their free Google My Business listing. Google My Business is a free directory of companies that can help smaller local businesses increase their visibility to searchers based on geolocation, a particularly important feature on mobile.
Ranking Signals and Search Algorithms
Organic results are listings that have been indexed by the search engine based on a number of factors, also known as “ranking signals.”
For example, the search algorithm used by Google features hundreds of ranking factors, and while nobody outside of Google knows precisely what they are, some are thought to be more important than others. In the past, the link profile of a site – the number of external links that link to a specific website or web page from other websites – was an important ranking signal. It still is to some extent (which is why Wikipedia ranks so prominently in organic results for so many queries), though search advances at such a rapid pace that ranking signals that were once crucial to the search algorithm may be less important today, a source of constant frustration to SEOs.
Search Engine Optimization and SERPs
As its name implies, search engine optimization is the practice of optimizing websites and web pages for discovery in search engines and, as a result, more visible placement on search engine results pages. This is accomplished through a variety of means, from what is known as “on-page” SEO to “off-page” techniques.
On-Page SEO
On-page SEO refers to best practices that web content creators and site owners can follow to ensure their content is as easily discoverable as possible. This includes the creation of detailed page metadata (data about data) for each page and elements such as images, the use of unique, static URLs, the inclusion of keywords in relevant headings and subheadings, and the use of clean HTML code, to name a few.
Off-Page SEO
Unlike on-page SEO techniques, off-page SEO refers to strategies that affect the site as a whole. Common off-page SEO techniques include link building and exchange, social bookmarking, content marketing, submissions to directories and search engine indexes, and the creation of online communities on social media.
Although the full scope of SEO is far too broad to cover comprehensively here, all you need to know is that SEO focuses primarily on achieving higher rankings from an organic perspective. Businesses may hire an agency or SEO professional to perform their SEO work, but beyond this investment, no money changes hands and all the emphasis is placed on ranking more highly in organic search.
PPC and Search Engine Results Pages
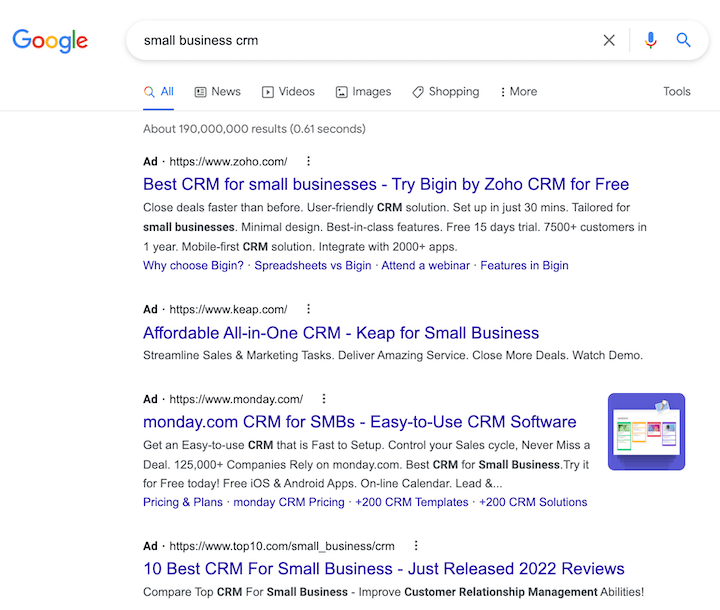
Unlike SEO, pay-per-click marketing focuses solely on the investment of advertising budget to achieve prominent positioning on search engine results pages. However, it’s not as simple as merely throwing more money at a campaign – advertisers must think strategically to achieve their goals.
Paid search functions as an auction. Advertisers bid on keywords that are relevant to their business that can trigger the display of their ads when users search for those terms. A wide range of factors determine where an ad will be shown on the SERP. Some ads might be displayed above the organic search results (such as the Lowe’s, Craftsman, and Husqvarna examples in the “lawnmowers” SERP example above), whereas others may be shown to the right of the organic results. Some advertisers choose to limit the display of their ads to mobile searches only, whereas others exclude mobile results altogether. Some ads feature extensions, and some do not.
Like SEO, paid search is a complex topic, but for now, just remember that paid search focuses on optimizing ads to be shown in as prominent a position on the SERP as possible.
Own the SERP
Want your ads to show up at the top of the SERP? Learn more about how we can help.
